What is Science Talent By Dr.Ying?
Science Talent By Dr.Ying is an innovative educational program designed to nurture and enhance students' scientific abilities. It offers a comprehensive curriculum that covers various scientific disciplines, aiming to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. The program is tailored to engage students through interactive and hands-on learning experiences, making science both fun and educational. With a focus on fostering a deep understanding of scientific concepts, Science Talent By Dr.Ying prepares students for future academic and career success in the field of science.
One of the standout aspects of Science Talent By Dr.Ying is its dynamic approach to teaching science. The program incorporates a variety of learning methods, including experiments, projects, and collaborative activities, to cater to different learning styles. Students benefit from personalized feedback and support, ensuring they grasp complex scientific ideas effectively. Additionally, the program is designed to align with educational standards, providing a structured yet flexible learning environment that encourages exploration and curiosity.
In schools, Science Talent By Dr.Ying is typically implemented as part of the science curriculum, either as a standalone program or integrated into existing courses. Teachers receive training and resources to effectively deliver the program, ensuring a seamless integration into the classroom. The program's adaptability allows it to be customized to fit the specific needs and goals of each school, making it a versatile choice for enhancing science education. By fostering a passion for science, Science Talent By Dr.Ying helps schools cultivate the next generation of scientific thinkers and innovators.
Compare Science Talent By Dr.Ying with...
Science Talent By Dr.Ying Reviews
No reviews.
This product has not received any reviews yet. Be the first!
Pedagogy
Certified by Education Alliance Finland,
EAF Evaluation is an academically-backed approach to evaluating the pedagogical design of a product. EAF evaluators assess the product using criteria that covers the most essential pedagogical aspects in the learning experience.
Learning goals
Certified by Education Alliance Finland
The supported learning goals are identified by mapping the product against the selected reference curriculum and soft skills definitions most relevant for the 21st century.
- Identify that most living things live in habitats to which they are suited and describe.
- Observe and describe how seeds and bulbs grow into mature plants.
- Identify and name a variety of everyday materials, including wood, plastic, glass, metal, water, and rock.
- Find out and describe how plants need water, light and a suitable temperature to grow and stay healthy.
- Identify and compare the suitability of a variety of everyday materials, including wood, metal, plastic, glass, brick, rock, paper and cardboard for particular uses.
- Encouraging the growth of positive self-image
- Identifying and classifying.
- Encouraging to build new information and visions
- Encouraging to build new information and visions
- Practicing to use foreign language as a communication tool
- Enabling the growth of positive self-image
- Using their observations and ideas to suggest answers to questions.
- Describe the simple physical properties of a variety of everyday materials.
- Compare and group together a variety of everyday materials on the basis of their simple physical properties.
- How different habitats provide for the basic needs of different kinds of animals and plants, and how they depend on each other.
- Identify and name a variety of common animals including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals.
- Learning to notice causal connections
- Practising visual recognition
- Practicing to observe spoken and written language
- Practicing categorization and classification
- Observing closely, using simple equipment.
- Practicing memorizing skills
- Practicing letters, alphabets and written language
- Identify and describe the basic structure of a variety of common flowering plants, including trees.
- Identify and name a variety of plants and animals in their habitats, including microhabitats.
- Distinguish between an object and the material from which it is made.
- Using technology for interaction and collaboration
- Learning to face failures and disappointments
- Practicing logical reasoning, algorithms and programming through making
- Use the idea that light travels in straight lines to explain why shadows have the same shape as the objects that cast them.
- Explain that we see things because light travels from light sources to our eyes or from light sources to objects and then to our eyes.
- Use the idea that light travels in straight lines to explain that objects are seen because they give out or reflect light into the eye.
- Recognise that light appears to travel in straight lines.
- Identify how animals and plants are adapted to suit their environment in different ways and that adaptation may lead to evolution.
- Recognise that living things produce offspring of the same kind, but normally offspring vary and are not identical to their parents.
- Describe the ways in which nutrients and water are transported within animals, including humans.
- Recognise the impact of diet, exercise, drugs and lifestyle on the way their bodies function.
- Identify and name the main parts of the human circulatory system, and describe the functions of the heart, blood vessels and blood.
- Explain that unsupported objects fall towards the Earth because of the force of gravity acting between the Earth and the falling object.
- Use the idea of the Earth’s rotation to explain day and night and the apparent movement of the sun across the sky.
- Describe the Sun, Earth and Moon as approximately spherical bodies.
- Describe the movement of the Moon relative to the Earth.
- Describe the movement of the Earth, and other planets, relative to the Sun in the solar system.
- Describe the life process of reproduction in some plants and animals.
- Identify common appliances that run on electricity.
- Find patterns between the pitch of a sound and features of the object that produced it.
- Identify how sounds are made, associating some of them with something vibrating.
- Identify the part played by evaporation and condensation in the water cycle and associate the rate of evaporation with temperature.
- Observe that some materials change state when they are heated or cooled, and measure or research the temperature at which this happens in degrees Celsius (°C).
- Compare and group materials together, according to whether they are solids, liquids or gases.
- Construct and interpret a variety of food chains, identifying producers, predators and prey.
- Identify the different types of teeth in humans and their simple functions.
- Describe the simple functions of the basic parts of the digestive system in humans.
- Recognise that environments can change and that this can sometimes pose dangers to living things.
- Explore and use classification keys to help group, identify and name a variety of living things in their local and wider environment.
- Recognise that living things can be grouped in a variety of ways.
- Predict whether two magnets will attract or repel each other, depending on which poles are facing.
- Describe magnets as having two poles.
- Compare and group together a variety of everyday materials on the basis of whether they are attracted to a magnet, and identify some magnetic materials.
- Observe how magnets attract or repel each other and attract some materials and not others.
- Notice that some forces need contact between two objects, but magnetic forces can act at a distance.
- Compare how things move on different surfaces.
- Find patterns in the way that the size of shadows change.
- Recognise that shadows are formed when the light from a light source is blocked by an opaque object.
- Recognise that light from the sun can be dangerous and that there are ways to protect their eyes.
- Notice that light is reflected from surfaces.
- Recognise that they need light in order to see things and that dark is the absence of light.
- Recognise that soils are made from rocks and organic matter.
- Compare and group together different kinds of rocks on the basis of their appearance and simple physical properties.
- Identify that humans and some other animals have skeletons and muscles for support, protection and movement.
- Identify that animals, including humans, need the right types and amount of nutrition, and that they cannot make their own food; they get nutrition from what they eat.
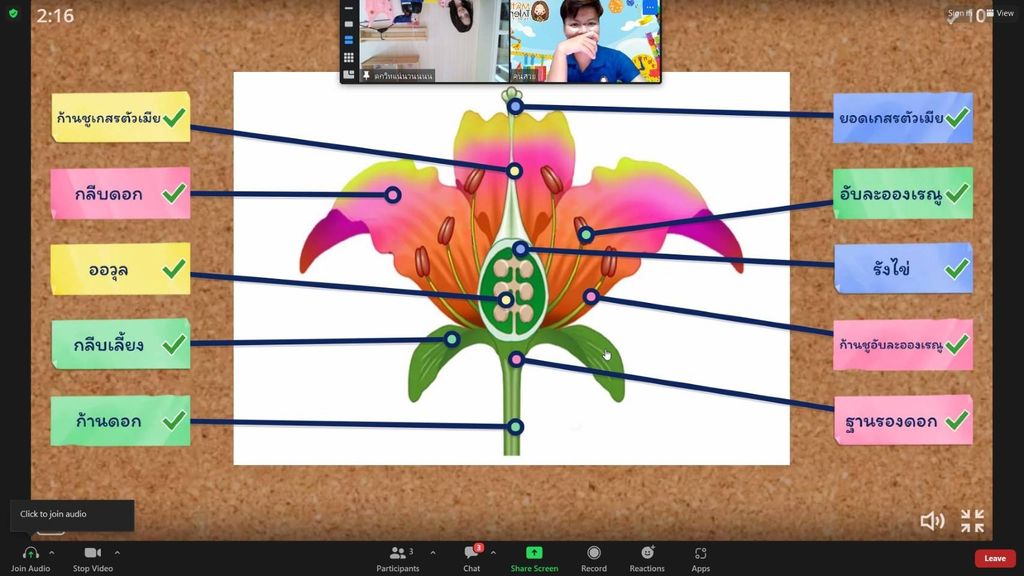
- Explore the part that flowers play in the life cycle of flowering plants, including pollination, seed formation and seed dispersal.
- Investigate the way in which water is transported within plants.
- Explore the requirements of plants for life and growth (air, light, water, nutrients from soil, and room to grow) and how they vary from plant to plant.
- Identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants: roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers.
- Find out how the shapes of solid objects made from some materials can be changed by squashing, bending, twisting and stretching.
- Identify and compare the suitability of a variety of everyday materials, including wood, metal, plastic, glass, brick, rock, paper and cardboard for particular uses.
- Describe the importance for humans of exercise, eating the right amounts of different types of food, and hygiene.
- Find out about and describe the basic needs of animals, including humans, for survival (water, food and air).
- Notice that animals, including humans, have offspring which grow into adults.
- Find out and describe how plants need water, light and a suitable temperature to grow and stay healthy.
- Observe and describe how seeds and bulbs grow into mature plants.
- Describe how animals obtain their food from plants and other animals, using the idea of a simple food chain, and identify and name different sources of food.
- Identify and name a variety of plants and animals in their habitats, including microhabitats.
- How different habitats provide for the basic needs of different kinds of animals and plants, and how they depend on each other.
- Identify that most living things live in habitats to which they are suited and describe.
- Compare and group together a variety of everyday materials on the basis of their simple physical properties.
- Describe the simple physical properties of a variety of everyday materials.
- Identify and name a variety of everyday materials, including wood, plastic, glass, metal, water, and rock.
- Distinguish between an object and the material from which it is made.
- Identify and name a variety of common animals including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals.
- Identify and describe the basic structure of a variety of common flowering plants, including trees.
- Identify and name a variety of common wild and garden plants, including deciduous and evergreen trees.
- Learning to notice causal connections
- Practising visual recognition
- Practicing categorization and classification
- Practicing fine motor skills
- Practicing memorizing skills
- Practicing letters, alphabets and written language
- Learning the basics of spelling
- Understanding and interpreting of matrices and diagrams
- Practicing to give, get and reflect feedback
- Practicing to express own thoughts and feelings
- Practicing to argument clearly own opinions and reasonings
- Encouraging to build new information and visions
- Learning about different languages
- Practicing to notice links between subjects learned
- Learning to combine information to find new innovations
- Encouraging to build new information and visions
- Learning to build information on top of previously learned
- Practicing to notice causal connections
- Practicing to recognize and express feelings
- Encouraging to build new information and visions
- How different habitats provide for the basic needs of different kinds of animals and plants, and how they depend on each other.
- Practicing keyboard skills and touch typing
- Practicing to use foreign language as a communication tool
- Practicing to take care of one's own wellbeing and health
- Supporting the growth of environmental awareness
- Recognizing habits that are good for sustainable living
- Use the idea of the Earth’s rotation to explain day and night and the apparent movement of the sun across the sky.
- Recognise that living things produce offspring of the same kind, but normally offspring vary and are not identical to their parents.
- Recognise the impact of diet, exercise, drugs and lifestyle on the way their bodies function.
- Describe the Sun, Earth and Moon as approximately spherical bodies.
- Identify and name the main parts of the human circulatory system, and describe the functions of the heart, blood vessels and blood.
- Recognise some common conductors and insulators, and associate metals with being good conductors.
- Identify common appliances that run on electricity.
- Practicing to observe spoken and written language
- Describe how animals obtain their food from plants and other animals, using the idea of a simple food chain, and identify and name different sources of food.
- Explain that unsupported objects fall towards the Earth because of the force of gravity acting between the Earth and the falling object.
- Find out and describe how plants need water, light and a suitable temperature to grow and stay healthy.
- Use the idea that light travels in straight lines to explain why shadows have the same shape as the objects that cast them.
- Describe the simple functions of the basic parts of the digestive system in humans.
- Supporting student to build their own linguistic and cultural identity
- Find patterns between the volume of a sound and the strength of the vibrations that produced it.
- Distinguish between an object and the material from which it is made.
- Learning about different languages
- Find out about and describe the basic needs of animals, including humans, for survival (water, food and air).
- Explore and use classification keys to help group, identify and name a variety of living things in their local and wider environment.
- Recognise that living things can be grouped in a variety of ways.
- Learning to view and consider media and advertising critically
- Learning to understand and interpret diverse types of texts
- Identify and describe the basic structure of a variety of common flowering plants, including trees.
- Explore the part that flowers play in the life cycle of flowering plants, including pollination, seed formation and seed dispersal.
- Encouraging to build new information and visions
- Observe changes across the four seasons.
- Identify and name a variety of everyday materials, including wood, plastic, glass, metal, water, and rock.
- Identify that most living things live in habitats to which they are suited and describe.
- Explore and compare the differences between things that are living, dead, and things that have never been alive.
- Observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies.
- Practicing to plan and execute studies, make observations and measurements
- Identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants: roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers.
- Explore the requirements of plants for life and growth (air, light, water, nutrients from soil, and room to grow) and how they vary from plant to plant.
- identify and name a variety of common animals that are carnivores, herbivores and omnivores.
- Identify that animals, including humans, need the right types and amount of nutrition, and that they cannot make their own food; they get nutrition from what they eat.
- Describe the life process of reproduction in some plants and animals.
- Identify and name a variety of common animals including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals.
- Practicing to use imagination and to be innovative
- Identify and name a variety of common wild and garden plants, including deciduous and evergreen trees.
- Encouraging students to be innovative and express new ideas
- Practicing to improvise
- Describe how living things are classified into broad groups according to common observable characteristics and based on similarities and differences, including microorganisms, plants and animals.
- Creating requirements for creative thinking
- Learning to find the joy of learning and new challenges
- Practicing to evaluate one's own learning
- Practicing to set one's own learning goals
- Practicing to take responsibility of one's own learning
- Understanding and practicing safe and responsible uses of technology
- Practicing persistent working
- Learning to listen other people’s opinions
- Practising visual recognition
- Practicing categorization and classification
- Practicing memorizing skills
- Practicing letters, alphabets and written language
- Practicing to find, evaluate and share information
- Understanding technological system operations through making
- Practising to understand visual concepts and shapes and observe their qualities
- Learning to acquire, modify and produce information in different forms
- Identify how animals and plants are adapted to suit their environment in different ways and that adaptation may lead to evolution.
- Using technology resources for problem solving
- Learning to understand and interpret diverse types of texts, from vernacular to academic
- Practicing logical reasoning to understand and interpret information in different forms
- Identify and name a variety of plants and animals in their habitats, including microhabitats.
- Using technology for interaction and collaboration
- Using technological resources for finding and applying information
- Using technology as a part of explorative and creative process
- Building common knowledge of technological solutions and their meaning in everyday life
- Describe the simple physical properties of a variety of everyday materials.
- Compare and group together a variety of everyday materials on the basis of their simple physical properties.
- Describe the importance for humans of exercise, eating the right amounts of different types of food, and hygiene.
- Identify and compare the suitability of a variety of everyday materials, including wood, metal, plastic, glass, brick, rock, paper and cardboard for particular uses.
- Compare and group together different kinds of rocks on the basis of their appearance and simple physical properties.
- Enabling the growth of positive self-image
- Recognise that light from the sun can be dangerous and that there are ways to protect their eyes.
- Practicing communication through different channels
- Recognise that they need light in order to see things and that dark is the absence of light.
- Describe the changes as humans develop to old age.
- Practicing to work with others
- Learning to understand people, surroundings and phenomenons around us
- Learning the basics of spelling
- Compare and group together everyday materials on the basis of their properties, including their hardness, solubility, transparency, conductivity (electrical and thermal), and response to magnets.